动词的时态语态-高考英语知识点
yggk.net 免费分享:动词的时态语态-高考英语知识点
练习题:
时态:表示动作发生或存在状态以及表现方式的一种动词形式。
语态:用来说明主语和谓语之间关系的一种动词形式。
主动语态表示句子的主语是动作的执行者或行为的主体;
被动语态表示主语是动作的承受者或行为的对象
英语中,在不同时间,以不同的方式发生的动作或存在的状态要用动词的不同形式表现出来,动词的这些不同形式构成了动词的时态。一般来说,发生在现在的事情用现在的时态进行描述,发生在过去的事情,用过去的时态进行描述,将要发生的事情用将来的时态进行描述。英语中的时态共计16种,常用的有12种。
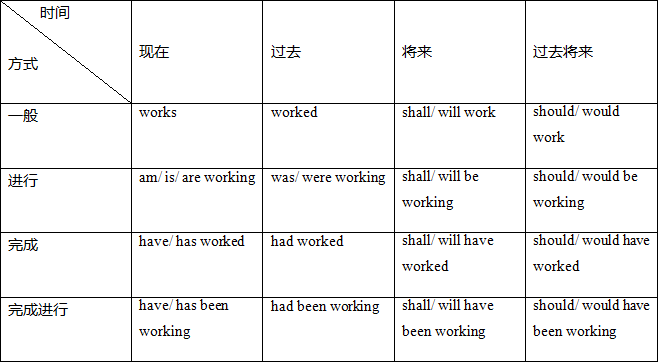

在高中阶段,我们将会主要学习到的时态有:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、现在完成进行时。本次课我们主要讲解一般现在时、一般过去时以及一般将来时
一.一般现在时
1.基本结构
肯定形式:
①be动词:am/is/are
②行为动词:动词原形、第三人称单数。
否定形式:
①am/is/are+not
②don't/doesn't+动词原形+……
一般疑问句:
①把be动词放于句首
②Do/Does+…+动词原形+…?
特殊疑问句:
特殊疑问词+一般疑问句
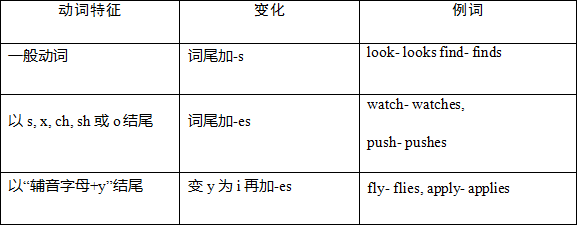
2.一般现在时的第三人称单数的构成:

3.基本用法:
① 表示经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语连用。时间状语有:always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays等。
例:I leave home for school at 7 every morning.
② 表示客观真理,客观存在或科学事实,以及格言或名言警句中。如:
The earth moves around the sun.
Shanghai lies in the east of China.
Failure is the mother of success. 失败乃成功之母。
③ 表示爱好、能力、性格、个性。
I like Chinese food.
I don't want so much.
Ann Wang writes good English but does not speak well.
4. 特殊用法
① 一般现在时代替将来时
1. 时间状语从句、条件状语从句用一般现在时代替将来时。如:when, before, after, till, once, as soon as, if, in case (that), unless,等。
He is going to visit her aunt the day he arrives in Beijing. 他一到北京,就去看他姨妈。I will call you as soon as I go back home. 我一到家就给你电话。
注:1. 可以代替as soon as表示一……就的词语:the moment、the minute、immediately、instantly
2. 主句部分除了用一般将来时,还可以用祈使句以及情态动词
例:If you have any problem, please contact me. (主祈从现)
If you have any problem, you can contact me.(主情从现)
3. not…until用法总结:
A. sb didn't do sth until sb did sth.
I didn't go home until I finished my homework yesterday. 我昨天直到完成作业才回家
B. sb won't do sth until sb do/does sth.(主将从现)
I won't leave until you come tomorrow. 我明天会直到你过来才会离开。
练习:翻译下面的句子
1. 昨天修理完桌椅后,我们才回家。
答案:We didn't go home until we finished repairing desks and tables.
2. 有时候,直到珍贵的时刻成为了回忆,你才会真正认识到它的价值所在。
答案:Sometimes, you won't know the true value of a moment until it becomes a memory.
2. 用于表示较固定的,按计划、规定将要发生的动作,但只限于begin, come, go, leave, arrive, stop, return, close, open, take, start, take place 等少数动作。
例:The train leaves Beijing at six and arrives at Jinan at nine.
② 一般现在时代替进行时
句型:Here comes… ; There goes…
例:Look, here comes Mr. Li.
There goes the bell.
二. 一般过去时
1. 基本结构
肯定形式:
① be动词:was / were …
② 行为动词:动词的过去式
否定形式:
① was/ were + not
② didn't +动词原形
一般疑问句:
① was或were放于句首
② Did + … + 动词原形……?
特殊疑问句:
特殊疑问词+一般疑问句
2. 动词的过去式及过去分词的构成:
规则动词的变化:
规则动词的过去式和过去分词的构成方法是相同的。


3. 用法
① 表示过去某一具体时间发生的动作或存在的状态,常用的时间状语有last year, yesterday, just now, in +过去年份, a few years ago, in the past.
例:Yesterday, I saw my friends off at the airport.
② 表示过去的经常性、习惯性动作或状态,常用的时间状语有always, often, usually, sometimes, seldom, never等
例:I always got up late and never had enough time for breakfast when I was a child.
三. 一般将来时
结构+用法
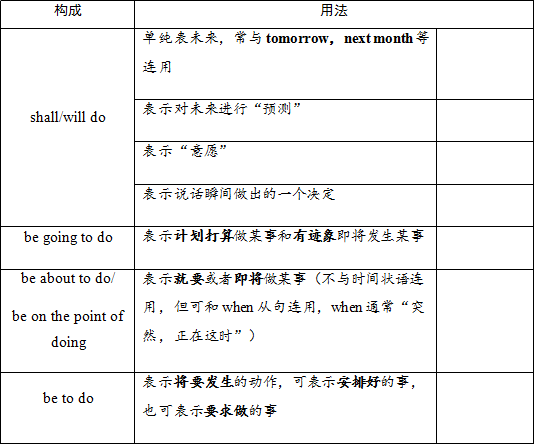
① "will/ shall + 动词原形"构成将来时,表示将要发生的动作或将要存在的状态。shall仅用于第一人称I/we作主语,而will 则用于各种人称。常用于将来时的时间状语有:next time, tomorrow, this afternoon, before long,in the future, soon, the day after tomorrow.
例:I shall visit my teacher when I go to Beijing.
② "be going to + 动词原形",表示打算、计划、安排做某事。
例:We are going to hold a sports meet next weekend.
③ begin, leave, arrive, start, finish, meet, return等动词的一般现在时,表示按计划或安排将要发生的事。(时刻表)
例:Flight 55 leaves at six p.m.
④ leave, go, come, stay, do, take, have 等动词的现在进行时,表示按计划或准备要做某事。
例:She is leaving early tomorrow morning. 明天她很早就出发。
⑤ "be to + 动词原形",表示即将发生某事、安排做某事或要求做某事。
例:The meeting is to take place at 8:00 tomorrow.
⑥ "be about + to+动词原形",表示即将发生某事,不与具体的将来时间状语连用
例:Hurry up! The train for Shanghai is about to start.
注意:1. shall/will do和be going to do的区别
shall/will do表示一种趋势或习惯性动作,或预言将要发生的事,或表示临时性打算等。
Fish will die without water.(趋势)
He will sit there doing nothing for hours.(习惯动作)
We haven't seen each other for a long time. Shall we have a dinner tonight?(临时性的打算)
be going to do表示提前计划、安排好的事情,或者表示有迹象发生
We are going to have a meeting at 8:00 tomorrow.(计划、安排)
Look at these clouds! It's going to rain.(迹象发生事情)
2. 一般现在时表将来和现在进行时表将来的区别
一般现在时表示计划、安排将要发生事情的时候主语通常为物(火车、飞机等-时刻表,有具体的时刻)
The train leaves Beijing at 7:00.
现在进行时表示计划、安排将要发生事情的时候主语通常为人。
They are having a meeting tonight.
练一练
1. 观察下列例句,将序号填入对应用法之后的空白栏中
A. 一般现在时
① All the living things on the earth depend on the sun.
② The plane takes off at 5:00 a.m.
③ Unless it rains tomorrow, the sports meet will take place.
④ Our teacher told us the earth goes round the sun.
⑤ He sometimes stay up till midnight to catch up with others.
⑥ We always care for each other and help each other.
⑦ She is a teacher.
⑧ -Do you sing? -A little.
B. 一般过去时
① I didn't know you bought the present for me.
② The Great Wall came into being in 221BC.
③ We used to get up at five every morning when we were at school.
④ When I was in the factory, I often worked in the workshop.
⑤ The professor put one finger in his mouth, tasted it, and smiled with satisfaction.
C. 一般将来时
① If you are going to do it, you had better do it well.
② If you will wait here, the manager will be back 10 minutes later.
③ We are to finish the work before five this afternoon.
④ He will be thirty years old next year.
⑤ No one is to leave the cinema without the police's permission
⑥ The train is about to start.
⑦ Look at the clouds, there is going to be a storm.
⑧ Will we clone a dinosaur?
⑨ You forgot to turn off the light!-Really, I will go and turn it off.

练习题: